Step 1: manage data confidence
A - Plan how to integrate confidence level aspect in the data and the processing objectives
- Understand confidence level. Three confidence levels exist for this type of data.
- Low Confidence (0-29%),
- Nominal Confidence (30-79%)
- High Confidence (80-100%)
- Calculate the confidence level attribute in the fire point layer
- Plan field name (conf_l)
- Count fire points in the administrative polygon layer for each confidence level
- Plan field names (nb_high_fire, nb_nominal_fire, nb_low_fire)
B - Calculate the confidence level attribute in the fire point layer
- Add algorithms
- Field calculator (rename it “Field calculator conf_l” to have a better management of your process)
- Calculate “conf_l” with an expression using “CONFIDENCE” attribute of the layer
- Input layer “Fire point layer”
- Field name: conf_l
- Type: string
- Length: 100
- Expression:
if("CONFIDENCE">30 and"CONFIDENCE"<80 ,'nominal',if("CONFIDENCE"<30,'low','high'))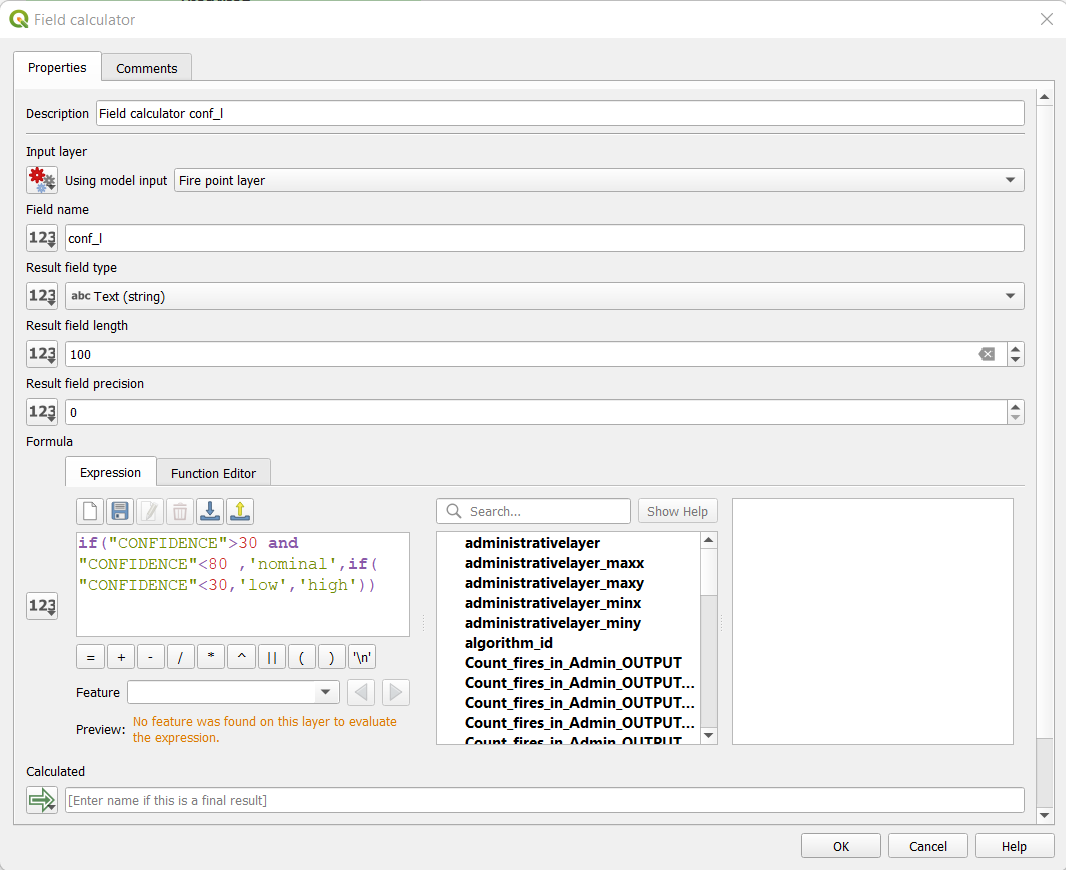
C - Count fire points in the administrative polygon layer for each confidence level
- Add algorithms
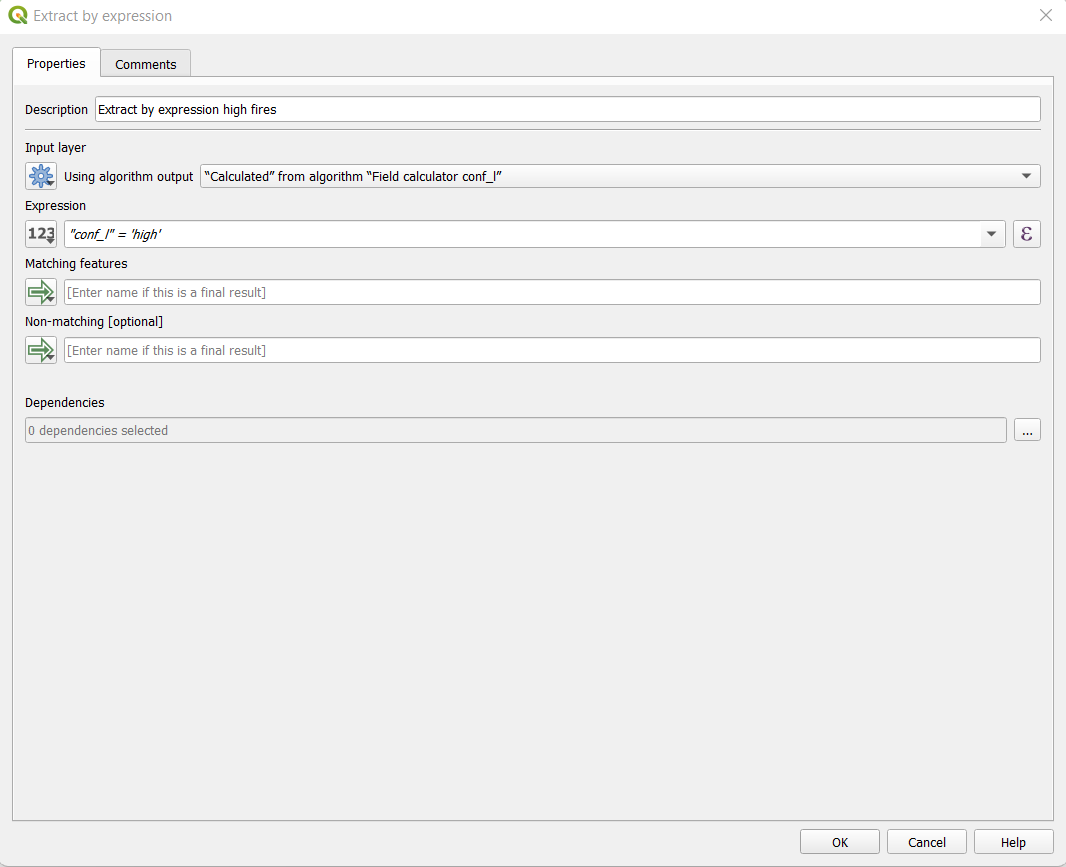
- Use 3 time Extract by expression (rename it to have a better management of your process, one for high fires, one for nominal fires and one for low fire), ex: “Extract by expression high fires”
- Select input layer (Using algorithm output): Calculated from algorithm “Field calculator conf_l”
- Set expression: “conf_l” = ‘high’
- Same for the other confidence level (nominal and low)
- Use 3 time Extract by expression (rename it to have a better management of your process, one for high fires, one for nominal fires and one for low fire), ex: “Extract by expression high fires”
💡You can copy, paste the algorithm selected in the Graphical modeller.
- Use 3 time Count point in polygons (rename it to have a better management of your process, one for high fires, one for nominal fires and one for low fire), ex: “Count point in polygon high fire”
- Modify the one we add in “Our first model” part
- Input polygon layer: administrative layer
- Input point layer: Matching features from algorithm “Extract by expression high fire”
- Count field name: nb_high_fire
- Do same for nominal fire
- Input polygon layer: Count from algorithm “Count point in polygon high fire”
- Input point layer: Matching features from algorithm “Extract by expression nominal fire”
- Count field name: nb_nominal_fire
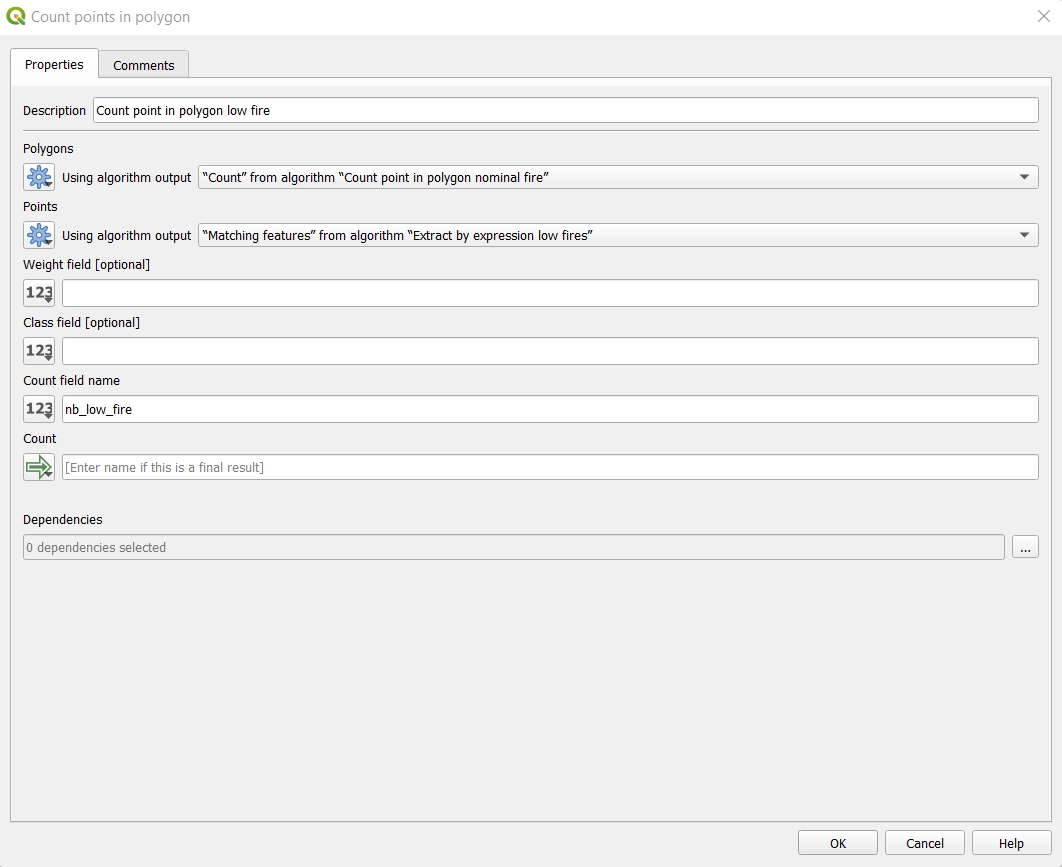
- Do same for low fire
- Input polygon layer: Count from algorithm “Count point in polygon nominal fire”
- Input point layer: Matching features from algorithm “Extract by expression low fire”
- Count field name: nb_low_fire
- Modify the one we add in “Our first model” part
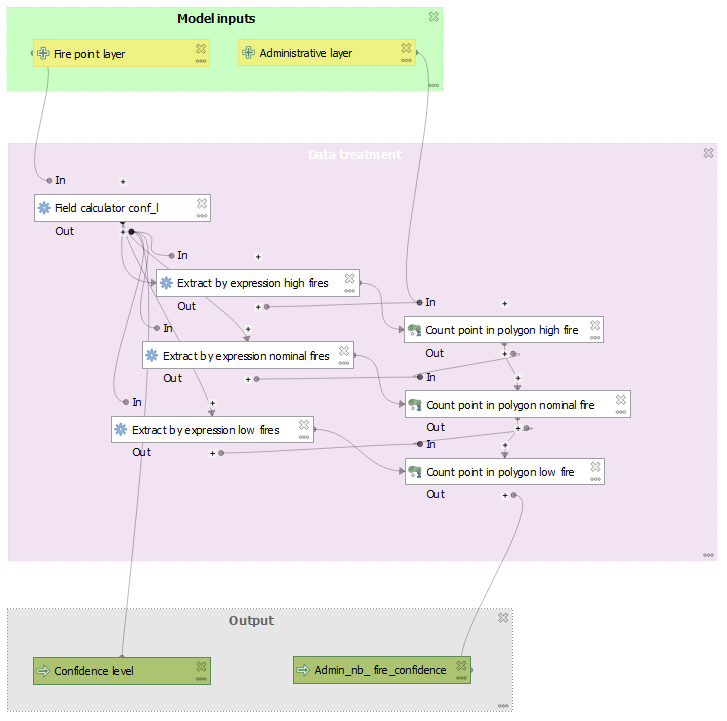
D - Manage algorithm dependencies to be sure they run in a proper order. Go to the first algorithm and click on the three dots of dependencies and select the algorithm parent.
- “Extract by expression high fire” depend “Field calculator conf_l”
- “Count point in polygon high fire” depend “Extract by expression high fire”
- “Extract by expression nominal fire” depend “Count point in polygon high fire”
- … until “Count point in polygon low fire”
E - Fill output name of “Field calculator conf_l” and “Count point in polygon low fire” algorithms
- Check if all calculated fields are ok
F - Save as you model, in case further developments break its execution. It will help you to get back on a solid base, if you mess up the processing.
Model output: Model_on_fire_v2.1.model3